DCHP-2
Green Paper green paper DCHP-2 (July 2016)
Non-Canadianism
n. — Politics
a government document that invites national public discussion on possible policy changes.
A Green Paper is defined as an official document sponsored by the Crown intended to spark national discussion on an issue prior to decisions on policy (see Parliament of Canada reference, s.v."Green Papers Introduction"). Thus, a Green Paper is formulated near the beginning of the policy-making process (see Canadian Encyclopedia, s.v. "Green Paper") and is followed by recommendations, consultation and ideally legislation (see the 2008 quotation). Examples of subjects discussed in Green Papers range from pension plans and health care to road safety and sales tax (see Parliament of Canada reference, s.v. "Green Paper Complete List").
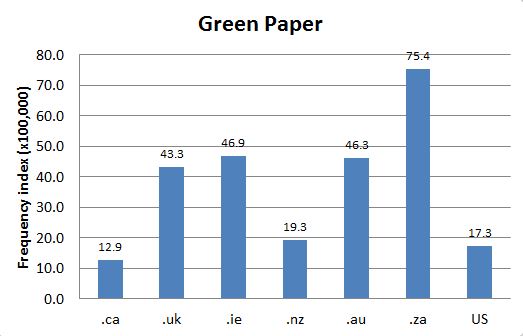
The term Green Paper is said to have been coined by London newspapers in Great Britain after their first introduction in 1967 (see Parliament of Canada reference, s.v."Green Papers Introduction"). Accordingly, OED-3 marks the term as used "in the United Kingdom and similar jurisdictions" (see OED-3, s.v. "Green Paper"), such as Canada (see Chart 1). The name apparently derives from the standard colour of document covers - green (see Parliament of Canada reference, s.v."Green Papers Introduction"). In Canada, however, Green Papers are more difficult to identify, as their title pages are not always green nor are they explicitly titled "Green Paper". Examples of titles of Green Papers in Canada include"Discussion Papers", "Consultation Papers", "Frameworks", "Visions", "Proposals" or "Strategies" (see Parliament of Canada reference, s.v. "Green Paper Complete List").
See also COD-2, s.v. "Green Paper", which is marked "Cdn & Brit." and Gage-5, s.v. "green paper", which is marked "Cdn."References:
- COD-2
- Canadian Encyclopedia s.v. "Green Paper" Accessed 2 Jun. 2016
- Gage-5
- OED-3
- Parliament of Canada "Green Papers Introduction" Accessed 27 May 2014
- Parliament of Canada "Green Papers Complete List" Accessed 27 May 2014
Images:
Chart 1: Internet Domain Search, 29 May 2014