DCHP-2
equality rights Equality Rights DCHP-2 (October 2016)
n. pl. — Law, Administration
a Canadian Charter guarantee that every individual receives equal treatment before the law without discrimination.
Type: 1. Origin — Equality rights are outlined in Section 15(1) of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms (see Justice Laws Canada reference, Part One of the Constitution Act of 1982, see Parliament of Canada reference). According to this section, all individuals possess the rights to "equal protection and equal benefit of the law" (see Government of Canada Publications reference) regardless of "race, ethnic origin, nationality, colour, religion, age, sex, mental or physical challenges". Moreover, equality rights also forbid discrimination on "analogous" grounds, or factors not outlined in section 15, such as sexual orientation or citizenship (see CBA-BC reference). The term equality rights replaced the term "non-discrimination rights" in the Charter (see the 1981 quotation) and section 15, known as the anti-discrimination clause (see Canadian Encyclopedia, s.v. "Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms"). Note that the Charter is not concerned with personal relationships or private businesses, as it relates to government actions and laws (see CRF reference).
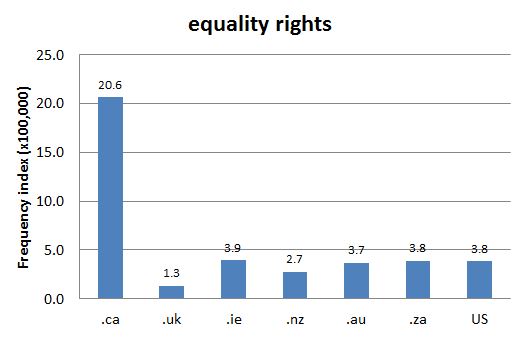
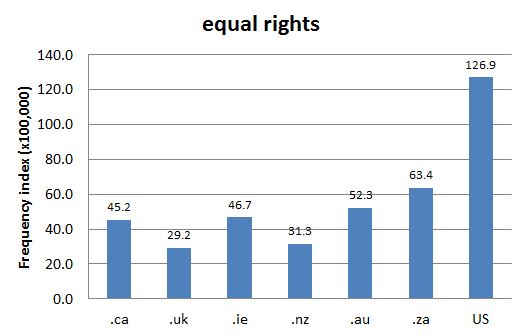
As seen in Chart 1, the term is most frequent in Canada, as elsewhere similar concepts are usually "equal rights" (see Chart 2).
See also COD-2, s.v. "equality rights", which is marked "Cdn Politics".See also: employment equity Charter
References:
- CBA-BC "Charter of Rights and Freedoms: Equality Rights " Accessed 27 May 2014
- COD-2
- CRF "Equality Rights" Accessed 27 May 2014
- Canadian Encyclopedia "Canadian Charter" Accessed 19 Apr. 2016
- Government of Canada Publications "Section 15 - Equality Rights" Accessed 27 May 2014
- Justice Laws Canada "CONSTITUTION ACT, 1982" Accessed 27 May 2014
- Parliament of Canada "Charter Equality Rights: Interpretation of Section 15" Accessed 4 Sep. 2013
Images:
Chart 1: Internet Domain Search, 27 May 2014
Chart 2: Internet Domain Search, 27 May 2014