DCHP-2
have province have-province, "have" province DCHP-2 (October 2016)
n. — Politics
a province which does not receive equalization payments from the federal government, because the average per capita tax revenue exceeds a set level; a "rich" province.
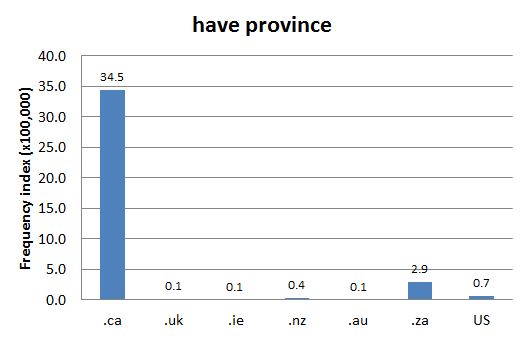
Type: 1. Origin — While the first federal equalization payments go back to 1957, these payments were entrenched in the 1982 constitution (see Canadian Encyclopedia reference). The concept of equalization is meant to limit 'horizontal' inequalities, i.e. inequalities that depend on where in the country a citizen lives. Provinces whose tax revenue is higher than a per capita cut-off set by the federal government are considered have provinces, i.e. "rich" provinces, and would be net payers in the federal system of transfer payments. The term appeared in the 1960s and is today overwhelmingly used in Canada (see Chart 1).
See COD-2, which labels the term "Cdn".See also: equalization have-not province transfer payment
References:
- COD-2
- Canadian Encyclopedia s.v. "Equalization Payments" Accessed 19 Nov. 2015
Images:
Chart 1: Internet Domain Search, 14 Aug. 2012